Knight
Medieval Knight
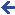
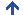
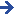
A knight was a member of the warrior class in the medieval Europe. The word knight is derived from Old English word cniht meaning “boy” or “servant”. This meaning is common among West Germanic languages, i.e. German and Duch – “knecht”, Danish Knaegt. In other Indo-European languages other words were used to describe knights, for example, in French chevalier or in German ritter. In Europe, knighthood was characterized by feudalism and service as a mounted warrior and both had their genesis during the reign of Frankish emperor Charlemagne. The medieval knights were asked to protect the weak, defenseless and helpless and to fight for the general welfare of all. Knights trained in fighting, riding and hunting and they were also trained to practice courteous and honorable behavior. The main principle that guided knight’s lifestyle was the code of Chivalry which dealt with three main areas: the military, religion and social life. A way of demonstrating military chivalry was to own very expensive heavy weaponry, armor and horses. Becoming a knight was not easy in the medieval era. Only the sons of a knight were eligible to join the ranks of knighthood.